A pelvic ultrasound is a safe, painless imaging test that uses sound waves to create detailed pictures of your reproductive organs and surrounding structures. This diagnostic tool helps doctors identify problems, monitor conditions, and guide treatment decisions for both men and women.
This guide is designed for patients scheduled for a pelvic ultrasound, family members seeking information, and anyone curious about what this common medical procedure involves. Whether you’re experiencing symptoms or need routine screening, understanding the process can help reduce anxiety and prepare you for your appointment.
We’ll walk you through the key medical reasons doctors order pelvic ultrasounds for men and women, covering everything from prostate issues to ovarian cysts. You’ll also learn what abnormal findings might look like on your scan and what they could mean for your health. Finally, we’ll cover the simple preparation steps you’ll need to follow and what actually happens during the exam, so you know exactly what to expect from start to finish.
Understanding Pelvic Ultrasound Technology and Types
How Sound Waves Create Detailed Pelvic Images
Pelvic ultrasound technology uses high-frequency sound waves, typically between 2-10 MHz, to create real-time images of internal structures. A transducer probe emits these sound pulses and captures their echoes as they bounce off different tissues. Denser tissues like bone reflect stronger signals, appearing white on the monitor, while fluid-filled areas appear dark or black, creating detailed contrast that helps identify abnormalities.
Transabdominal vs Transvaginal Ultrasound Methods
| Method | Approach | Best For | Preparation Required |
| Transabdominal | External probe on abdomen | Overall pelvic overview, bladder assessment | Full bladder required |
| Transvaginal | Internal probe insertion | Detailed uterine and ovarian imaging | Empty bladder preferred |
Transabdominal scanning provides broader coverage but requires a full bladder for optimal visualization. Transvaginal ultrasound offers superior resolution for female reproductive organs, positioning the probe closer to target structures for clearer, more detailed images.
Real-Time Imaging Capabilities for Dynamic Assessment
Real-time ultrasound capabilities allow doctors to observe organ movement and blood flow patterns instantly during examination. This dynamic assessment proves valuable for evaluating heart rate in developing fetuses, detecting ovarian cysts that change with movement, and assessing bladder function. The technology also enables guided procedures, where physicians can watch the probe’s position live while performing biopsies or other interventional techniques with enhanced precision and safety.
Essential Medical Purposes for Male Pelvic Ultrasounds
Detecting Prostate Enlargement and Abnormalities
Male pelvic ultrasounds serve as a primary diagnostic tool for identifying prostate-related conditions that affect millions of men worldwide. The procedure can detect benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), which causes urinary difficulties, and helps identify suspicious masses that may require further investigation. Doctors rely on ultrasound imaging to measure prostate size, assess gland texture, and evaluate blood flow patterns that might signal underlying health concerns.
Evaluating Bladder Function and Urinary Issues
Ultrasound technology provides valuable insights into bladder capacity, wall thickness, and post-void residual volume measurements. These assessments help diagnose urinary retention, bladder outlet obstruction, and other voiding dysfunctions that commonly affect older men. The non-invasive nature of ultrasound makes it an ideal first-line imaging method for investigating lower urinary tract symptoms.
Identifying Testicular Problems and Hernias
Scrotal ultrasounds can detect testicular masses, varicoceles, hydroceles, and epididymal cysts with remarkable accuracy. High-frequency sound waves produce detailed images that help differentiate between benign and potentially malignant conditions. Inguinal hernias and their complications can also be visualized, providing surgeons with essential pre-operative planning information.
Monitoring Post-Surgery Recovery Progress
Post-surgical monitoring becomes streamlined through regular ultrasound examinations that track healing progress and identify potential complications. Patients who’ve undergone prostate procedures, hernia repairs, or other pelvic surgeries benefit from this safe imaging method. The ability to perform repeated scans without radiation exposure makes ultrasound particularly valuable for long-term follow-up and for adjusting treatment decisions.
Critical Medical Purposes for Female Pelvic Ultrasounds
Monitoring Pregnancy Development and Fetal Health
Pregnancy monitoring represents the most common reason for female pelvic ultrasounds, offering critical insights into fetal development and maternal health. During the first trimester, ultrasounds confirm pregnancy viability, establish gestational age, and detect multiple pregnancies. Second and third-trimester scans assess fetal growth, organ development, and placental position while screening for potential complications like placental abruption or cervical insufficiency.
These examinations also monitor amniotic fluid levels, fetal heart rate patterns, and umbilical cord positioning. Healthcare providers use Doppler ultrasound to evaluate blood flow to the placenta and fetus, ensuring adequate oxygen and nutrient delivery. Regular monitoring helps identify growth restrictions, birth defects, or positioning issues that may require special delivery considerations or immediate medical intervention.
Diagnosing Ovarian Cysts and Reproductive Disorders
Ovarian cysts affect millions of women annually, ranging from benign functional cysts to complex masses requiring surgical intervention. Ultrasound technology distinguishes between simple fluid-filled cysts and more concerning solid or mixed-density masses. The examination evaluates cyst size, internal structure, and blood flow patterns to determine appropriate treatment approaches, from watchful waiting to immediate surgical removal.
Reproductive disorders like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) appear clearly on ultrasound imaging through characteristic ovarian appearance and increased follicle counts. Other conditions including ovarian torsion, dermoid cysts, and endometriomas each present distinct ultrasound features that guide diagnosis and treatment decisions. Early detection through routine screening significantly improves treatment outcomes and fertility preservation options.
Evaluating Uterine Fibroids and Endometrial Issues
Uterine fibroids affect up to 80% of women by age 50, causing symptoms ranging from heavy bleeding to pelvic pressure and fertility challenges. Ultrasound mapping identifies fibroid location, size, and number while distinguishing between intramural, subserosal, and submucosal types. This classification directly impacts treatment selection, whether medication management, minimally invasive procedures, or surgical removal becomes necessary.
Endometrial evaluation through ultrasound measures lining thickness and identifies abnormal growths like polyps or hyperplasia. Saline infusion sonography provides enhanced visualization of intrauterine abnormalities that standard ultrasound might miss. These assessments help diagnose causes of abnormal uterine bleeding, particularly important for postmenopausal women where endometrial cancer screening becomes critical for early detection and treatment success.
Detecting Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) creates serious reproductive health complications when left untreated, including chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility. Ultrasound imaging reveals characteristic signs like thickened fallopian tubes, fluid collections, and complex ovarian masses that indicate active or chronic infection. These findings help distinguish PID from other conditions presenting similar symptoms, ensuring appropriate antibiotic treatment begins promptly.
Chronic PID complications appear as hydrosalpinx (fluid-filled tubes) or tubo-ovarian abscesses requiring different treatment approaches than acute infections. Ultrasound monitoring tracks treatment response and identifies patients needing surgical intervention. Early diagnosis through imaging prevents long-term reproductive consequences and reduces the risk of life-threatening complications like sepsis or abscess rupture that require emergency medical care.
Assessing Fertility-Related Concerns
Fertility evaluations rely heavily on ultrasound imaging to assess ovarian reserve, follicular development, and uterine structure. Antral follicle counts predict ovarian response to fertility treatments, while endometrial thickness measurements determine optimal timing for embryo transfer or natural conception attempts. These assessments guide personalized fertility treatment protocols and help predict success rates for various interventions.
Structural abnormalities like septate uterus, bicornuate uterus, or blocked fallopian tubes significantly impact conception chances and pregnancy outcomes. Detailed ultrasound mapping identifies these conditions early in fertility workups, allowing corrective procedures when appropriate. Regular monitoring during fertility treatments tracks follicle growth, ovulation timing, and early pregnancy development, maximizing treatment effectiveness while minimizing risks associated with ovarian hyperstimulation or multiple pregnancies.
Common Abnormal Findings in Male Patients
Enlarged Prostate Gland Indicators
Male pelvic ultrasounds commonly reveal enlarged prostate glands, particularly in men over 50. This condition, called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), appears as increased prostate size on imaging, often accompanied by bladder wall thickening due to increased effort during urination.
Kidney Stones and Urinary Blockages
Ultrasound effectively identifies kidney stones and related obstructions throughout the urinary tract. These appear as bright, echogenic spots that cast acoustic shadows. Blockages can cause kidney swelling (hydronephrosis) and backup of urine, creating potentially serious complications requiring immediate medical attention.
Fluid Accumulation in Pelvic Cavity
Abnormal fluid collections in the male pelvis may indicate infection, inflammation, or trauma. Ultrasound shows these as dark, echo-free areas that can suggest conditions like prostatitis, post-surgical complications, or pelvic abscesses requiring targeted treatment approaches.
Frequent Abnormal Findings in Female Patients
Ovarian Cysts and Tumor Detection
Pelvic ultrasounds excel at spotting ovarian abnormalities, from simple fluid-filled cysts to complex masses requiring immediate attention. Simple cysts appear as dark, round spaces and often resolve naturally, while solid or mixed-consistency masses may signal tumors needing biopsy. The scan measures size, evaluates internal structure, and checks blood flow patterns to help doctors distinguish between benign conditions and potential malignancies.
Uterine Fibroids and Polyp Identification
Fibroids show up as well-defined masses within the uterine wall, ranging from pea-sized to grapefruit-sized growths that can cause heavy bleeding and pain. Polyps appear as finger-like projections extending into the uterine cavity, often causing irregular bleeding between periods. Both conditions are clearly visible on ultrasound, allowing doctors to map their exact location, size, and number for treatment planning.
Ectopic Pregnancy Warning Signs
Ectopic pregnancies create distinctive ultrasound patterns that emergency physicians watch for carefully. The scan reveals an empty uterus despite positive pregnancy tests, while showing fluid accumulation in the pelvis or a gestational sac in the fallopian tube. Early detection prevents life-threatening rupture and internal bleeding.
Pelvic Organ Prolapse Assessment
Specialized ultrasound techniques measure how pelvic organs shift during straining, revealing bladder, uterine, or rectal prolapse. The scan shows organ displacement and helps surgeons plan repair procedures. Dynamic imaging captures real-time movement, providing crucial information about pelvic floor weakness that physical exams might miss.
Pre-Examination Preparation Requirements

Optimal Bladder Filling Guidelines for Clear Images
Your bladder needs to be moderately full for a pelvic ultrasound, which acts like a window that helps the technologist see your internal organs clearly. Drink 32 ounces of water about one hour before your appointment, then avoid urinating until after the exam. The full bladder pushes gas away from the pelvic area and provides better image quality.
Dietary Restrictions to Minimize Gas Interference
Skip gas-producing foods like beans, carbonated drinks, dairy products, and high-fiber foods for 24 hours before your exam. Gas bubbles can block sound waves and create poor image quality. Stick to light, easily digestible meals and avoid chewing gum or using straws, which can introduce extra air into your digestive system.
Clothing and Jewelry Removal Instructions
Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothes that allow easy access to your abdomen and pelvis. Remove all jewelry from your waist down, including belts, body piercings, and metal accessories that might interfere with the ultrasound equipment. Two-piece outfits work best since you’ll only need to expose the examination area while keeping your upper body covered.
Medication Considerations Before Your Appointment
Take your regular medications as prescribed unless your doctor specifically tells you otherwise. Blood pressure medications, diabetes drugs, and heart medications should not be skipped. If you’re taking medications for digestive issues or pain relievers, discuss timing with your physician since some can affect gas production or bladder function during the exam.
What to Expect During Your Ultrasound Procedure
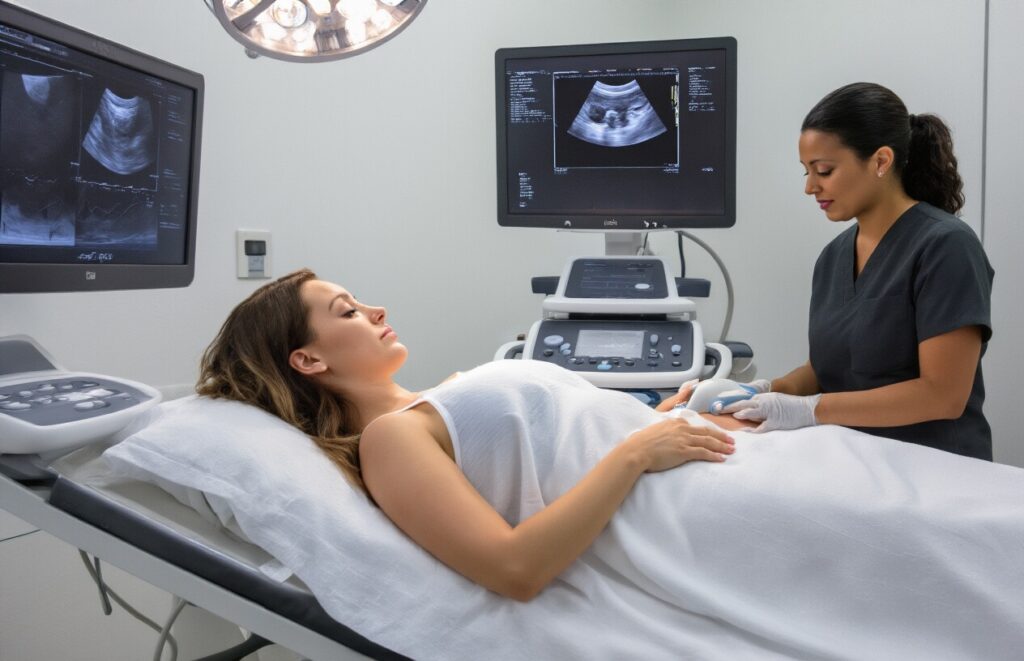
Step-by-Step Examination Process
Your ultrasound technician will ask you to change into a hospital gown and position yourself on an examination table. For transabdominal scans, you’ll lie on your back with your abdomen exposed. The technician will dim the room lights to better visualize the monitor images. During transvaginal examinations for female patients, you’ll be positioned similarly to a gynecological exam with your feet in stirrups.
Gel Application and Probe Positioning
A clear, water-based gel gets applied to your skin to eliminate air pockets between the transducer and your body. This gel feels cool initially but warms quickly to body temperature. The technician will move the probe across your lower abdomen or insert it vaginally, applying gentle pressure to capture optimal images of your pelvic organs and surrounding structures.
Duration and Comfort Measures
Most pelvic ultrasounds take 15-30 minutes to complete, depending on the complexity of your case. You can breathe normally throughout the procedure, though the technician may ask you to hold your breath briefly for clearer images. The examination is painless, though you might experience mild pressure from the probe. The gel wipes off easily with towels provided after your scan.
Interpreting Your Ultrasound Results Effectively
Normal vs Abnormal Finding Classifications
Your ultrasound report categorizes findings as normal, abnormal, or requiring follow-up. Normal results show organs with typical size, shape, and position without masses or fluid collections. Abnormal findings include cysts, tumors, enlarged organs, or structural irregularities that may need treatment or monitoring.
When Follow-Up Testing May Be Recommended
Doctors recommend additional testing when ultrasound results show suspicious masses, unexplained symptoms, or inconclusive findings. Follow-up might include MRI scans, CT imaging, or specialized ultrasounds. Your physician considers your symptoms, medical history, and initial ultrasound results when determining next steps for your care and diagnosis.
Understanding Technical Terms in Your Report
| Term | Meaning |
| Echogenic | Appears bright on ultrasound |
| Hypoechoic | Appears dark or low-density |
| Heterogeneous | Mixed texture or appearance |
| Fluid collection | Abnormal fluid accumulation |
Common terms like “unremarkable” mean normal, while “prominent” suggests enlargement. Your radiologist uses specific measurements and descriptions to communicate findings clearly to your physician for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Pelvic ultrasounds serve as powerful diagnostic tools that help doctors get a clear picture of what’s happening inside your body. Whether you’re dealing with unexplained pain, fertility concerns, or routine health monitoring, this safe and non-invasive procedure can reveal important information about your reproductive organs, bladder, and surrounding tissues. From detecting ovarian cysts and prostate issues to monitoring pregnancies and investigating urinary problems, ultrasounds give physicians the insights they need to make accurate diagnoses and create effective treatment plans.
Getting ready for your pelvic ultrasound is straightforward – just follow your doctor’s instructions about drinking water or emptying your bladder beforehand. The actual procedure is quick and painless, and you’ll have your results soon after. Remember that abnormal findings don’t automatically mean something serious is wrong; many conditions detected through ultrasound are easily treatable when caught early. If your doctor recommends a pelvic ultrasound, don’t hesitate to ask questions about what to expect and what the results might mean for your health journey.


