“Understanding MRI Angiography of Carotid Vessels With Contrast – Purpose, Procedure & Benefits”
MRI angiography carotid vessels with contrast offers a powerful, non-invasive way to examine blood flow and detect blockages in the carotid arteries without surgical procedures. This advanced imaging technique uses gadolinium contrast MRI to create detailed pictures of your carotid vessels, helping doctors spot carotid stenosis MRI signs and other vascular problems early.
This guide is written for patients scheduled for carotid artery imaging, family members supporting loved ones through the process, and anyone wanting to understand this important diagnostic tool for carotid artery disease detection.
We’ll walk you through how contrast enhanced carotid MRI technology works and why doctors recommend it for carotid artery blockage diagnosis. You’ll learn what to expect during your MRA carotid vessels exam, including preparation steps and safety considerations. Finally, we’ll help you understand your carotid MRI angiogram results and how doctors use these findings to create your treatment plan.
Understanding MRI Angiography Technology for Carotid Assessment
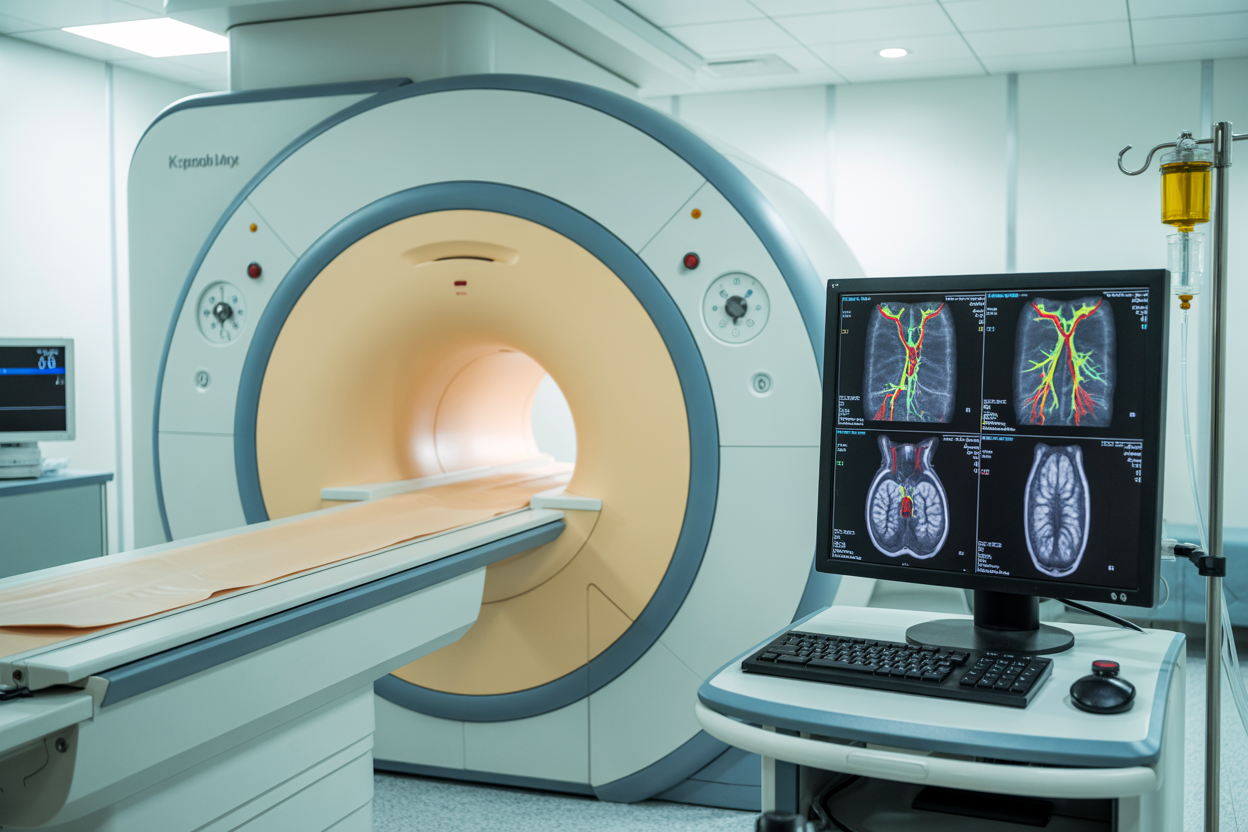
How MRI angiography creates detailed blood vessel images
MRI angiography carotid imaging works by detecting the movement of blood through your arteries using powerful magnetic fields and radio waves. When you receive a contrast enhanced carotid MRI, the gadolinium contrast agent acts like a beacon, making your blood vessels light up brightly on the scan images. This contrast material travels through your bloodstream and creates a stark difference between the flowing blood and surrounding tissues.
The MRI scanner captures multiple images as the contrast moves through your carotid arteries, creating a real-time movie of blood flow. This process allows doctors to see exactly how blood moves through your neck vessels and identify any areas where flow might be restricted or blocked. The technology can detect carotid stenosis MRI abnormalities as small as 1-2 millimeters, making it incredibly precise for carotid artery disease detection.
Unlike traditional angiography that requires catheter insertion, MRA carotid vessels imaging is completely non-invasive vascular imaging. The scanner builds three-dimensional maps of your arteries by combining hundreds of thin-slice images, giving doctors a complete picture of your vascular anatomy. This detailed visualization helps identify plaque buildup, narrowed arteries, and other abnormalities that could lead to stroke.
Advanced imaging sequences used in carotid evaluation
Modern carotid artery imaging employs several specialized MRI sequences to capture different aspects of blood vessel health. Time-of-flight (TOF) sequences detect moving blood without contrast by using the natural flow properties of blood cells. This technique works particularly well for identifying carotid artery blockage diagnosis in the neck region where blood flow is typically robust.
Contrast-enhanced MRA sequences provide the most detailed images by using gadolinium contrast MRI technology. These sequences can be timed precisely to capture arterial, capillary, and venous phases of blood flow, giving doctors a comprehensive view of circulation patterns. The timing is critical – images captured too early or too late might miss important details about blood flow dynamics.
Phase-contrast MRA measures the actual velocity and direction of blood flow within your arteries. This sequence helps doctors understand not just where blockages exist, but how severely they’re affecting blood flow. Black-blood sequences suppress the blood signal to better visualize arterial walls and identify plaque composition, helping determine whether deposits are stable or prone to rupture.
Multi-planar reconstruction techniques allow radiologists to view your carotid arteries from multiple angles, rotating and tilting the images to examine vessels from every direction. This comprehensive approach ensures that no abnormalities are missed during evaluation.
Medical Benefits of Contrast-Enhanced Carotid MRI Angiography
Superior visualization of arterial narrowing and blockages
Contrast-enhanced carotid MRI angiography revolutionizes how doctors see inside your carotid arteries, providing crystal-clear images that reveal even the smallest problems. When gadolinium contrast is injected during the scan, it acts like a highlighter for your blood vessels, making them stand out dramatically against surrounding tissues. This enhanced visibility allows radiologists to spot arterial narrowing as subtle as 10-15%, which might go unnoticed with other imaging methods.
The contrast agent flows through your carotid vessels, illuminating every curve and potential trouble spot. Areas where plaque has built up appear as darker regions against the bright blood flow, creating a detailed roadmap of your vascular health. This level of detail proves especially valuable when assessing carotid stenosis, as doctors can measure the exact degree of narrowing and determine whether surgical intervention might be necessary.
Unlike traditional angiography that requires inserting catheters directly into arteries, contrast enhanced carotid MRI offers the same diagnostic precision without invasive procedures. The three-dimensional images produced show your carotid arteries from multiple angles, helping physicians distinguish between soft plaque that might rupture and calcified deposits that remain more stable. This comprehensive view enables accurate assessment of both the severity and composition of any blockages present.
Early detection of stroke risk factors
MRA carotid vessels imaging with contrast serves as a powerful early warning system for stroke prevention. The procedure can identify dangerous plaque formations years before they cause symptoms, giving you and your medical team valuable time to implement preventive strategies. Research shows that detecting carotid artery disease in its early stages dramatically improves treatment outcomes and reduces stroke risk.
The enhanced imaging capabilities reveal subtle changes in arterial walls that signal developing atherosclerosis. Small areas of irregular plaque buildup, minor vessel wall thickening, and early signs of inflammation become visible long before they progress to critical stenosis levels. This early detection proves particularly important since carotid artery blockage diagnosis often occurs after significant narrowing has already developed.
Contrast-enhanced scans also identify patients at risk for plaque rupture, a leading cause of embolic strokes. The imaging shows plaque characteristics that indicate instability, such as thin fibrous caps or lipid-rich cores. Armed with this information, doctors can prescribe appropriate medications, recommend lifestyle changes, or schedule more frequent monitoring to prevent stroke occurrence.
Regular screening with carotid artery imaging helps track disease progression over time, allowing medical teams to adjust treatment plans as needed. This proactive approach transforms stroke prevention from reactive care to predictive medicine, potentially saving lives through early intervention.
Patient Preparation and Safety Considerations

Pre-scan screening for contrast allergies and kidney function
Before your contrast enhanced carotid MRI, your medical team will conduct a thorough screening to ensure the gadolinium contrast MRI procedure is safe for you. Your radiologist needs to know about any previous reactions to contrast materials, even from CT scans or other imaging studies. While gadolinium-based contrast agents used in carotid artery imaging are generally safer than iodine-based contrasts, allergic reactions can still occur, ranging from mild skin reactions to more serious breathing difficulties.
Kidney function testing is crucial because your kidneys filter out the contrast agent after the scan. Your doctor will likely order blood tests to check your creatinine levels and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) within 30 days of your MRA carotid vessels appointment. If you have chronic kidney disease, diabetes, or are over 60, these tests become even more important. Patients with severely reduced kidney function might need alternative non-invasive vascular imaging approaches or require special pre-treatment protocols.
Don’t forget to mention any medications you’re taking, especially those affecting kidney function like blood pressure medications, diabetes drugs, or anti-inflammatory medications. Your healthcare provider might also ask about recent illnesses, dehydration, or other procedures that could impact your kidney function. Being upfront about your complete medical history helps ensure your carotid stenosis MRI proceeds safely and provides the clearest possible images for accurate carotid artery disease detection.
Medication adjustments before your appointment
Several medications can interfere with your carotid MRI angiogram results or increase risks during the procedure. Your doctor will review your complete medication list and may ask you to temporarily adjust certain prescriptions before your scan.
If you’re taking metformin for diabetes, your healthcare provider might recommend stopping it 48 hours before and after your contrast-enhanced study. This precaution helps prevent a rare but serious condition called lactic acidosis, especially if your kidney function becomes temporarily affected by the contrast agent. Blood thinners like warfarin, newer anticoagulants, or even aspirin typically don’t need to be stopped for MRI angiography carotid imaging since this is a non-invasive procedure.
Diuretics (water pills) might need temporary adjustment since dehydration can stress your kidneys when processing contrast material. Your doctor may suggest increasing your fluid intake in the days leading up to your appointment. Some blood pressure medications, particularly ACE inhibitors or ARBs, might be temporarily held depending on your kidney function and overall health status.
Always bring a complete list of your medications, including over-the-counter supplements, vitamins, and herbal remedies. Some supplements can affect kidney function or interact with contrast agents. Never stop prescribed medications without explicit instructions from your healthcare team, as this could create more serious health risks than the imaging procedure itself.
Interpreting Your Carotid MRI Angiography Results
Normal versus abnormal findings explained
When you receive your carotid MRI angiography results, your radiologist looks for several key features that distinguish healthy blood vessels from problematic ones. Normal carotid arteries appear as smooth, uninterrupted channels with consistent diameter throughout their length. The contrast enhancement should be uniform, creating bright, well-defined vessel walls without any irregularities or gaps in the signal.
Abnormal findings in contrast enhanced carotid MRI typically include areas of narrowing (stenosis), complete blockages (occlusions), or irregular vessel walls indicating plaque buildup. Your radiologist will identify any disruptions in the smooth flow of contrast material, which shows up as dark spots or irregular narrowing within the bright vessel outline. Plaque deposits appear as areas of reduced signal intensity along the vessel walls, sometimes creating a “string of beads” appearance in severely affected arteries.
The MRA carotid vessels imaging can also reveal other concerning features like dissections, where the artery wall has torn, or aneurysms, where the vessel has abnormally widened. Ulcerated plaques, which carry higher stroke risk, appear as irregular crater-like depressions in the vessel wall. Your report will describe the location, extent, and characteristics of any abnormalities found, helping your doctor understand your specific risk profile for stroke or other vascular complications.
Understanding stenosis percentages and clinical significance
Carotid stenosis MRI measurements follow standardized criteria that correlate directly with your stroke risk and treatment needs. Stenosis percentages represent how much of the normal vessel diameter has been reduced by plaque buildup. Mild stenosis ranges from 30-49% narrowing and typically requires monitoring with lifestyle modifications and medication management. This level rarely causes immediate symptoms but warrants attention to prevent progression.
Moderate stenosis falls between 50-69% narrowing and represents a more significant concern. Patients with moderate stenosis often benefit from aggressive medical therapy, including blood thinners, cholesterol medications, and blood pressure control. Your doctor will likely recommend more frequent monitoring through repeat imaging studies.
Severe stenosis, measuring 70% or greater narrowing, carries substantial stroke risk and often requires intervention. The carotid artery blockage diagnosis at this level means your brain receives significantly reduced blood flow through that vessel. Many patients with severe stenosis become candidates for carotid endarterectomy (surgical plaque removal) or carotid stenting procedures.
Critical stenosis above 90% narrowing represents imminent stroke risk, often requiring urgent intervention. The non-invasive vascular imaging helps your vascular surgeon plan the safest approach for treatment. Your carotid MRI angiogram results will include precise measurements, allowing your medical team to track changes over time and determine optimal treatment timing. Even small changes in stenosis percentage can significantly impact treatment decisions and stroke prevention strategies.
Treatment Planning Based on MRI Angiography Findings
Conservative management for mild stenosis
When your MRA carotid vessels results show mild stenosis (typically less than 50% blockage), doctors usually recommend a conservative approach that focuses on slowing disease progression and preventing complications. The detailed imaging from contrast enhanced carotid MRI helps physicians determine the exact degree of narrowing and develop personalized treatment strategies.
Medication management forms the cornerstone of conservative treatment. Antiplatelet therapy, commonly aspirin or clopidogrel, reduces blood clot formation risk. Statins play a crucial role in stabilizing arterial plaques and lowering cholesterol levels that contribute to carotid stenosis MRI findings. Blood pressure medications help reduce strain on already compromised vessels, while diabetes management prevents additional vascular damage.
Lifestyle modifications work alongside medications to address underlying risk factors. Smoking cessation remains the most impactful change patients can make, as tobacco use accelerates arterial narrowing. Regular exercise improves circulation and helps develop collateral blood flow around partially blocked areas. Dietary changes focusing on heart-healthy foods reduce inflammation and slow plaque buildup.
Regular monitoring through follow-up MRI angiography carotid imaging typically occurs every 6-12 months for mild stenosis cases. This surveillance approach allows doctors to track progression and adjust treatment before symptoms develop. The non-invasive vascular imaging capabilities of gadolinium contrast MRI make this ongoing assessment both safe and highly accurate for detecting changes in vessel narrowing over time.
Surgical intervention criteria for severe blockages
Severe carotid artery blockage diagnosis through MRI angiography requires immediate evaluation for surgical intervention. When imaging reveals stenosis greater than 70% in symptomatic patients or 80% in asymptomatic individuals, surgical options become the primary treatment consideration. The high-resolution images from carotid MRI angiogram results provide surgeons with detailed anatomical information needed for procedure planning.
Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) remains the gold standard surgical treatment for eligible patients. This procedure involves surgically opening the artery and removing the plaque buildup identified through carotid artery imaging. Candidates for CEA typically have good overall health, reasonable life expectancy, and favorable anatomical features visible on their MRA studies. The detailed vessel mapping from contrast-enhanced imaging helps surgeons identify the exact location and extent of plaque for optimal surgical planning.
Carotid artery stenting (CAS) offers an alternative for patients who aren’t ideal CEA candidates due to medical comorbidities or anatomical challenges. This minimally invasive procedure uses the detailed roadmap provided by carotid stenosis MRI to guide catheter placement and stent deployment. High-risk surgical candidates, those with previous neck surgery, or patients with lesions in difficult-to-reach locations often benefit from this approach.
Patient selection criteria extend beyond stenosis percentage alone. Symptomatic patients who’ve experienced transient ischemic attacks or strokes related to their carotid artery disease detection have different risk-benefit calculations than asymptomatic individuals. Age, overall health status, and life expectancy factor into surgical decision-making, with the detailed imaging from MRI angiography providing objective data to support these complex treatment decisions.
MRI angiography with contrast offers a powerful, non-invasive way to examine your carotid vessels and catch potential problems before they become serious health issues. This advanced imaging technology gives doctors crystal-clear pictures of blood flow and vessel structure, helping them spot blockages, narrowing, or other abnormalities that could lead to stroke or other complications. The contrast enhancement makes even small details visible, giving your medical team the complete picture they need for accurate diagnosis.
If your doctor has recommended carotid MRI angiography, know that proper preparation and understanding what to expect can make the experience much smoother. The detailed images from this scan become the roadmap for your treatment plan, whether that means lifestyle changes, medication, or surgical intervention. Don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare provider questions about your results and next steps – being an active participant in your care leads to better outcomes and peace of mind about your vascular health.


