“HRCT Chest Explained: Detecting Lung Infections, Fibrosis, and Interstitial Lung Diseases”
HRCT chest scans offer detailed, high-resolution images of your lungs and surrounding chest structures, helping doctors detect and monitor various respiratory conditions with exceptional clarity.
This guide is designed for patients scheduled for an HRCT chest scan, family members seeking information about the procedure, and anyone wanting to understand how this advanced imaging technology works. We’ll walk you through what makes HRCT chest different from regular CT scans and why doctors recommend this specific test for lung-related concerns.
You’ll discover the key medical conditions that HRCT chest can diagnose, from early-stage lung diseases to complex respiratory disorders that might not show up on standard X-rays. We’ll also cover how to prepare for your scan and what the entire process looks like from start to finish.
Finally, we’ll explain how to understand your HRCT chest results and what steps typically follow once your doctor reviews the images, helping you feel confident and informed throughout your diagnostic journey.
Understanding HRCT Chest Technology and Benefits
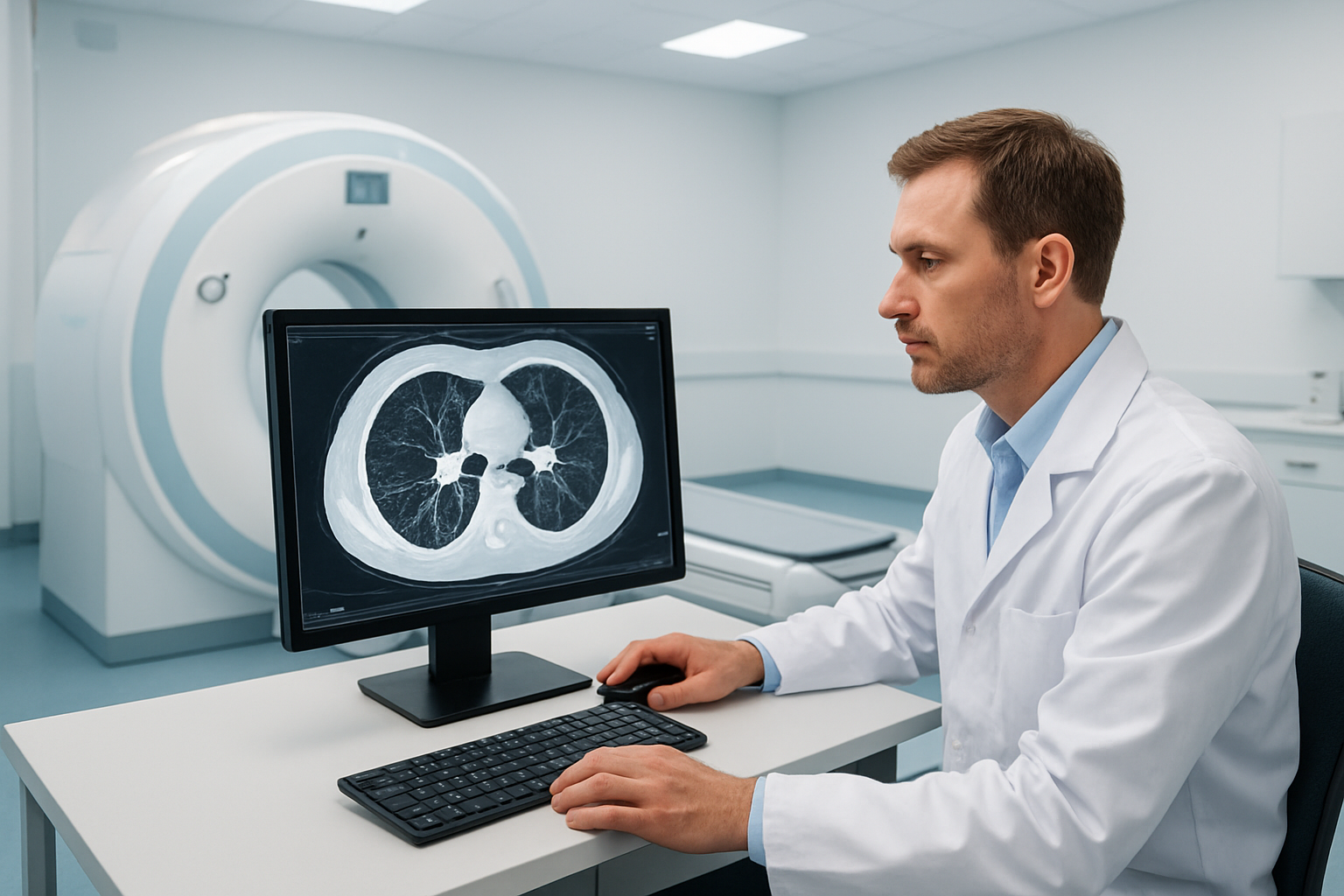
Advanced Imaging Capabilities Beyond Standard CT Scans
High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) chest scans represent a significant leap forward from conventional CT imaging technology. This specialized scanning technique captures incredibly detailed cross-sectional images of the chest cavity, focusing specifically on the lung tissue with remarkable precision.
The key difference lies in the technical specifications. HRCT uses thin-section imaging protocols, typically with slice thickness of 1-1.5mm compared to standard CT scans that use 5-10mm slices. This dramatic reduction in slice thickness means doctors can examine lung structures at a microscopic level, revealing details that would be completely missed on regular chest X-rays or standard CT scans.
The scanning algorithms are specifically optimized for lung tissue evaluation. Unlike standard CT scans that prioritize overall chest anatomy, HRCT employs specialized reconstruction techniques that enhance the contrast between different lung tissues. This allows radiologists to distinguish between healthy lung tissue, inflammation, scarring, and various pathological changes with extraordinary clarity.
Modern HRCT technology also incorporates advanced dose reduction protocols, ensuring patients receive minimal radiation exposure while maintaining superior image quality. The digital processing capabilities create images with enhanced spatial resolution, making it possible to detect abnormalities measuring just a few millimeters in size.
Many CGHS empanelled facilities now offer this advanced imaging technology, making it accessible to government employees and pensioners. The digital nature of modern HRCT systems enables quick report generation and sharing through secure channels.
Superior Detection of Lung Abnormalities and Diseases
HRCT chest imaging excels at identifying lung conditions that remain invisible on standard imaging studies. The enhanced resolution capabilities make it the gold standard for diagnosing interstitial lung diseases, early-stage lung cancers, and subtle inflammatory conditions.
For pulmonary infections, HRCT can distinguish between different types of pneumonia, identify complications like abscesses or empyema, and track treatment response. The detailed imaging helps doctors differentiate between viral, bacterial, and fungal infections based on specific patterns and distributions within the lung tissue.
Occupational lung diseases, such as silicosis or asbestosis, show characteristic patterns on HRCT that help establish both diagnosis and disease progression. The scan can detect these conditions years before symptoms appear, allowing for early intervention and workplace safety modifications.
Early-stage lung cancer detection represents another crucial advantage. HRCT can identify pulmonary nodules as small as 2-3mm, enabling early treatment when cure rates are highest. The detailed imaging also helps characterize nodules, determining which ones require immediate attention versus routine monitoring.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) assessment through HRCT provides detailed information about disease severity, pattern, and progression. The scans reveal emphysema distribution, airway wall thickening, and help guide treatment decisions.
At modern diagnostic facilities, HRCT reports are delivered digitally via WhatsApp for immediate access, while physical films can be collected from the centre at your convenience. This efficient system ensures both healthcare providers and patients receive timely results for prompt medical decision-making.
Key Medical Conditions Diagnosed Through HRCT Chest
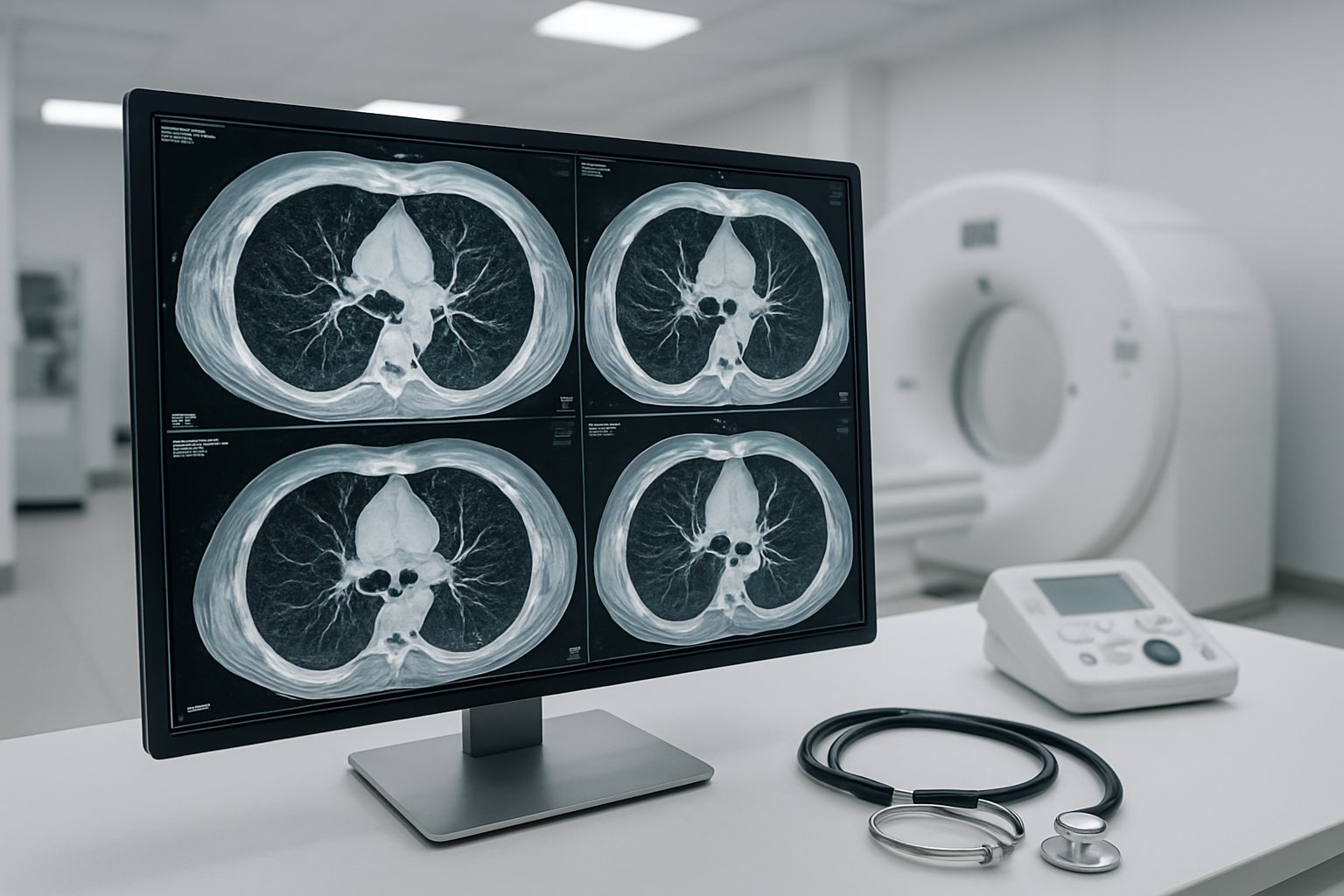
Early Detection of Pulmonary Fibrosis and Interstitial Lung Diseases
HRCT chest scans excel at catching pulmonary fibrosis in its earliest stages, often before patients notice significant symptoms. Traditional chest X-rays miss up to 90% of early fibrotic changes, while HRCT can detect subtle scarring patterns that measure just millimeters in size. This early detection capability proves crucial since pulmonary fibrosis progresses rapidly once established, and treatment works best when started early.
The scan reveals characteristic patterns that help doctors distinguish between different types of interstitial lung diseases:
- Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP): Shows honeycomb patterns and subpleural distribution
- Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia (NSIP): Displays ground-glass opacities with lower lobe preference
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Presents with centrilobular nodules and air trapping
- Sarcoidosis: Demonstrates hilar lymphadenopathy with upper lobe nodular patterns
HRCT also tracks disease progression with remarkable precision. Serial scans can measure changes in lung density and identify new areas of inflammation before they become irreversible scarring. Doctors use quantitative analysis software to calculate the percentage of affected lung tissue, providing objective data for treatment decisions.
For patients with occupational exposures like asbestos or silica dust, HRCT serves as a screening tool that can detect pneumoconiosis decades before symptoms appear. The scan’s ability to differentiate between active inflammation and established fibrosis helps guide whether patients need anti-inflammatory treatments or supportive care.
Comprehensive Evaluation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
HRCT revolutionizes COPD assessment by revealing structural changes that pulmonary function tests can’t detect. While spirometry measures airflow limitation, HRCT visualizes the actual damage to lung tissue, providing a complete picture of disease severity and distribution patterns.
The scan identifies two main COPD phenotypes with different treatment approaches:
| COPD Phenotype | HRCT Findings | Clinical Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Emphysema-dominant | Low attenuation areas, bullae formation | Higher risk for pneumothorax, different surgical options |
| Bronchitis-dominant | Airway wall thickening, mucus plugging | Better response to bronchodilators and mucolytics |
HRCT detects emphysema when it affects as little as 5% of lung tissue, compared to chest X-rays which require 30-40% involvement. The scan maps emphysema distribution patterns – upper lobe predominance suggests smoking-related damage, while lower lobe patterns point to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
Airways assessment through HRCT reveals bronchial wall thickening, bronchiectasis, and small airway disease that standard imaging misses. These findings explain why some COPD patients experience frequent exacerbations despite normal-appearing chest X-rays. The scan also identifies complications like pulmonary hypertension through enlarged pulmonary arteries and lung cancer screening in high-risk patients.
Quantitative CT analysis measures lung density automatically, providing objective metrics for disease monitoring. This data helps predict which patients might benefit from lung volume reduction surgery or bronchoscopic interventions by identifying target areas with the most severe emphysematous destruction.
Preparing for Your HRCT Chest Examination
Essential pre-scan instructions and dietary restrictions
Your HRCT chest examination requires minimal preparation, making it a convenient diagnostic option. Unlike many other imaging procedures, you won’t need to fast or follow strict dietary restrictions before your scan. You can eat and drink normally on the day of your examination.
However, certain preparations will help ensure the best possible image quality. Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing without metal components like zippers, buttons, or underwire bras. Metal objects can create artifacts on your images, potentially affecting the diagnostic quality. If your clothing contains metal, the facility will provide a hospital gown for the procedure.
Remove all jewelry, watches, and metallic accessories before entering the scanning room. This includes hairpins, dentures with metal components, and hearing aids. Store these items securely in the provided lockers.
If you’re a CGHS beneficiary, bring your CGHS card and necessary documentation. Our facility is CGHS empanelled, which means you can receive your examination through the government health scheme. Contact our center beforehand to understand the authorization process and required paperwork.
Arrive at the facility 15-20 minutes before your scheduled appointment. This allows time for registration, changing clothes if needed, and completing any remaining paperwork. The staff will review your medical history and ensure you’re ready for the procedure.
Medication adjustments and contrast agent considerations
Most HRCT chest examinations don’t require contrast agents, so your regular medications typically won’t need adjustment. Continue taking your prescribed medications as usual unless specifically instructed otherwise by your referring physician.
However, inform the radiologist about all medications you’re currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. Some medications might interact with contrast agents if they become necessary during your examination, though this is uncommon for routine HRCT chest scans.
If you have diabetes and take metformin, discuss this with the facility staff during scheduling. While contrast isn’t routinely used for HRCT chest, having this information documented ensures proper protocol if circumstances change during your examination.
Bring a complete list of your current medications, including dosages and frequency. This helps the medical team make informed decisions about your care and ensures your safety throughout the procedure.
If you have severe kidney disease or are on dialysis, notify the center when scheduling your appointment. Though contrast agents are rarely needed for HRCT chest examinations, this information is important for your medical record and any future procedures that might be recommended.
After your examination, digital reports will be sent to you via WhatsApp for immediate access. You’ll need to visit the center at your convenience to collect the physical films of your scan. The staff will inform you about the timeline for report availability and film collection procedures.
What to Expect During the HRCT Chest Procedure
Step-by-step scanning process and positioning requirements
When you arrive for your HRCT chest scan, the radiologic technologist will first guide you to the CT scanner room. You’ll be asked to change into a hospital gown and remove any jewelry, metal objects, or clothing with metal fasteners that could interfere with the imaging process.
The CT scanner looks like a large donut-shaped machine with a movable table. The technologist will help position you on the examination table, typically lying on your back with your arms raised above your head. This arm positioning is crucial because it moves your arms out of the scan field, preventing them from blocking the view of your chest structures.
The table will then slide you into the scanner opening until your chest is properly aligned with the imaging equipment. The technologist will use laser lights to ensure precise positioning. You’ll notice the scanner makes a slight humming sound during operation, which is completely normal.
The actual scanning process is remarkably quick, usually taking only 10-15 seconds per breath-hold sequence. The entire examination typically lasts between 10-20 minutes, including positioning time. During the scan, thin X-ray beams rotate around your chest, capturing multiple cross-sectional images that create detailed pictures of your lungs, airways, and surrounding tissues.
Breathing instructions for optimal image quality
Breathing control plays a critical role in producing clear, diagnostic-quality images. The technologist will provide specific breathing instructions through an intercom system, and you’ll hear these directions clearly before each scan sequence begins.
For most HRCT chest scans, you’ll be asked to take a deep breath and hold it for approximately 10-15 seconds while the images are captured. This breath-holding eliminates motion blur that could obscure important details in your lung tissue. The technologist will usually say something like “take a deep breath in and hold it” followed by “breathe normally” when the sequence is complete.
Some examinations may require both inspiration (breathing in) and expiration (breathing out) images. During expiration scans, you’ll be instructed to breathe out completely and hold your breath out while the images are taken. These different breathing phases help radiologists evaluate how your lungs function and can reveal certain conditions that might not be visible on inspiration images alone.
If you have difficulty holding your breath due to respiratory conditions, inform the technologist beforehand. They can adjust the scanning protocol or provide additional support to help you achieve the best possible image quality while ensuring your comfort throughout the procedure.
Interpreting HRCT Chest Results and Next Steps
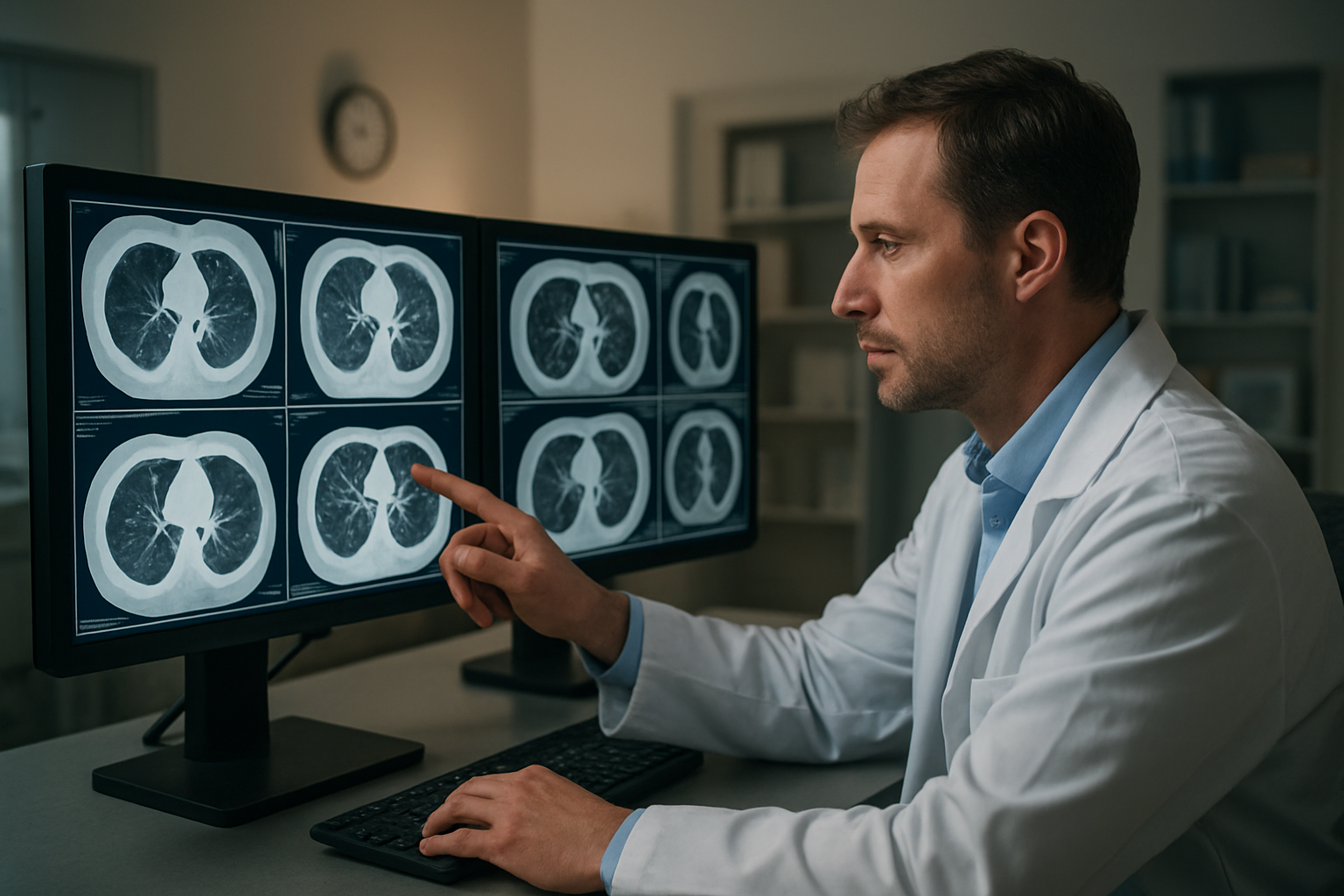
Understanding Radiologist Reports and Imaging Findings
When you receive your HRCT chest report, the language might seem overwhelming at first. Radiologists use specific medical terminology to describe what they observe in your chest images, and understanding these terms can help you better grasp your condition.
The report typically begins with technical details about the scan quality and patient positioning. The main findings section describes abnormalities in different areas of your lungs, including the upper, middle, and lower zones. Common terms you might encounter include “ground-glass opacity” which appears as hazy areas in the lungs, “consolidation” indicating filled air spaces, or “honeycombing” describing advanced scarring patterns.
Your radiologist will also comment on the pleura (lung lining), mediastinum (central chest area), and any lymph nodes. Terms like “bilateral” mean both lungs are affected, while “unilateral” refers to one side only. “Diffuse” indicates widespread changes, whereas “focal” describes localized areas of concern.
At our CGHS empanelled facility in Sector 65, Gurugram, we provide digital reports through WhatsApp for immediate access. This allows you to share findings quickly with your referring physician while you arrange to collect the physical films at your convenience. Our experienced radiologists ensure detailed reporting that helps your doctor make informed treatment decisions.
Comparing Results with Previous Scans for Disease Progression
Serial HRCT chest scans serve as a powerful tool for monitoring disease progression or improvement over time. When comparing current images with previous studies, radiologists look for specific changes in lung patterns, lesion sizes, and overall disease extent.
Progressive conditions like pulmonary fibrosis show characteristic changes over time. Early scans might reveal subtle ground-glass changes, while follow-up studies could demonstrate increasing reticulation, traction bronchiectasis, or honeycombing. Conversely, inflammatory conditions often show improvement with treatment, displaying reduced opacity or consolidation areas.
The comparison process involves measuring lesion dimensions, counting affected lung segments, and assessing functional changes. Radiologists create detailed comparison charts highlighting:
| Progression Indicators | Improvement Signs |
|---|---|
| Increasing opacity areas | Clearing of consolidation |
| New lesion development | Reduced ground-glass patterns |
| Growing lymph nodes | Decreased pleural effusion |
| Worsening scarring | Improved lung expansion |
Your doctor uses these comparative findings to adjust treatment plans, determine medication effectiveness, or decide on intervention timing. Some conditions require monitoring every 3-6 months, while others need annual follow-ups.
Our centre maintains comprehensive digital archives, making it easy to access and compare your historical scans. This continuity of care ensures accurate progression tracking and optimal treatment outcomes for our patients.
HRCT chest scans have become a game-changer for doctors when they need detailed images of your lungs and chest area. This advanced imaging technology helps catch lung problems early, gives doctors crystal-clear pictures to work with, and makes diagnosis much more accurate than regular chest X-rays. Whether you’re dealing with breathing issues, chronic cough, or your doctor suspects a lung condition, HRCT provides the detailed information needed for proper treatment planning.
Getting ready for your HRCT scan is straightforward, and the actual procedure is quick and painless. Once your scan is complete, you’ll receive your digital reports conveniently through WhatsApp, while physical films can be picked up from our centre at your convenience. For CGHS beneficiaries, our empanelled facility in Sector 65, Gurugram makes this advanced diagnostic service easily accessible. Talk to your doctor about whether an HRCT chest scan is right for you – early detection through proper imaging can make all the difference in your health outcomes.


